How to Decide Which Codon to Use for an Aminoacid
ENc is a metric that measures codon bias in terms of deviation from an assumed neutral distribution of synonymous codon usage. Amino Acids to Codons Conversion.
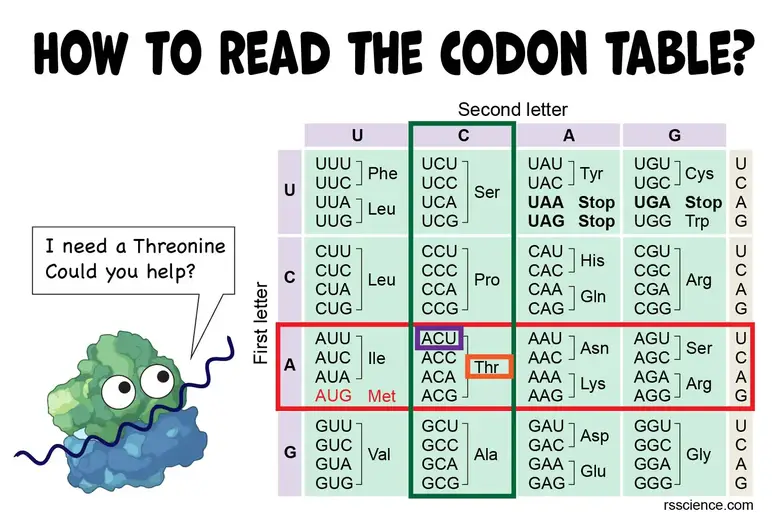
How To Read The Amino Acids Codon Chart Genetic Code And Mrna Translation Rs Science
The other 15 amino acids are coded by two three and four triplets.

. STEP 4 Use the below table to find the relevant amino acid. The formula used in amino acids to codons conversion is 1 Amino Acid 1 Codon. The DNA codons representing each amino acid are also listed.
The start codon marks the site at which translation into protein sequence begins and the stop codon marks the site at which translation ends. Three other triplets UAA UAG and UGA are stop sequences. Find the first letter of the codon triplet from the left side of the table.
Anti-codons in the template strand are identified as groups of three bases moving from the right end 5 end to the left end 3 end. That is moving in the direction. It is all due to physics and biochemistry.
Codon 2 reads ACG so the anticodon would read UGC. For some amino acids in some organisms we. Aa stands for amino acids and Codon stands for codons.
In addition many non-standard amino acids have a specific code. Would these be antiparallel. He suggested that genetic code should be made of three nucleotides which code for 20 amino acids with four bases.
Follow the example in the box. The genetic code is polar means that the code always read in a fixed direction. The ENc was calculated for all genomic coding.
Codon is the name we give a stretch of the three nucleotides you know one of A C G or T three of which in a row that code for a specific amino acid and so the genetic code is made up of units called codons where you have three nucleotides that code for a specific amino acid next to another three nucleotides another three nucleotides and another three. Using Coding strand. Codon 1 reads AUG.
Image from the NLM Associatesppt presentation October 2002 by Susan Dombrowski PhD. How are the right amino acids added in the right sequence to match the codon in the mRNA. You will see the corresponding amino acid.
The stop codon is the codon that gives end signals to terminate protein synthesis. All 64 possible 3-letter combinations of the DNA coding units T C A and G are used either to encode one of these amino acids or as one of the three stop codons that signals the end of a sequence. The right amino acid is carried by a tRNA molecule which also carries a complementary key its anticodon to the mRNA codon.
The 3 anticodon bases use complementary base pairing with 3 mRNA bases called a codon ie. On the other end is a set of 3 bases called an anticodon ie. Three stop codons mark the end of a protein.
While DNA can be decoded unambiguously it is not possible to predict a DNA sequence. To use an amino acid codon wheel start from the center and follow the RNA codons until you have the 3 nucleotide bases. Four nitrogenous bases and three nucleotides together form a triplet codon which codes for one amino acid.
For each amino acid we identified the most favored optimal codon defined as the codon that showed both the strongest and statistically significant positive Spearman correlation with the overall level of codon bias P005n where n is the number of codons encoding the amino acid in question Materials and Methods. Decode the DNA sequence. Use a Genetic Code table as in the next slide.
The process is called RNA translation. GCU and if they fit this is the correct tRNA molecule and therefore the correct amino acid. The corresponding tRNA would have an anticodon reading UAC.
For example several peptide drugs such as Bortezomib and MG132 are artificially synthesized and retain their protecting groups which have specific codes. Larger ENc values correspond to more equal usage of synonymous codons while the lowest possible ENc value would result from the case of one codon used for each amino acid. How to Use an Amino Acid Wheel.
Next translate the three bases into an amino acid from the mRNA codons. Find the third letter of the codon triplet in the box. One start codon AUG marks the beginning of a protein and also encodes the amino acid methionine.
How you begin to read the chart is you look at the left hand column in the row of A since that. On one end of the tRNA you will find an anti-codon. In fact one codon the codon is generated can be a code the same amino acid but the same codon shall not code for two or more different amino acids non-ambiguity.
Up to 24 cash back How you determine your amino acids are by these steps. Use your new code in this case it is AUG to read the chart. Answer 1 of 3.
Use your codon chart to determine the amino acid sequence. Once established follow the RNA sequence to find the amino acid that it translates to. If your DNA sequence is TAC then when you decode it it will translate into the RNA AUG.
Arginine leucine and serine each are coded by six triplets. Here are some features of codons. Find the second letter of the codon triplet from the upper axis of the table.
To convert all types of measurement units you can used this tool which is able to provide you conversions on a scale. Codons in an mRNA are read during translation. But we have 20 naturally existing amino acids.
Most codons specify an amino acid. Bortezomib is Pyz -Phe-boroLeu and MG132 is Z -Leu-Leu-Leu-al. We can see that we achieve the same sequence irrespective of the strand used.
To aid in the analysis of. For the Codons animation the left-most two base pairs are hidden leaving exactly five 3-base codons 15 base pairs. The genetic code describes the relationship between the sequence of DNA bases A C G and T in a gene and the corresponding protein sequence that it encodes.
Unk is sometimes used instead of Xaa but is less standard. Methionine and tryptophan each are coded by just one triplet. How do we know which codon codes for which amino acid.
Oppisite the anticodon you will find a binding site for a specific amino acid. The coding strand turns gray and then disappears leaving the template strand see strands above. A description of how to read to Genetic Code allowing you to translate an mRNA molecule into an polypeptide a chain of amino acids.
In other words 1 amino acid is 1 times smaller than a codon. Decode the DNA sequence. ALWAYS start from the codon AUG and NEVER count the same nucleotide twice.
Locate the intersect box of 1st row and 2nd column in the codon table. A U T A GC CG Read from left to right. STEP 3 Convert m-RNA as a sequence of codons.
The same amino acid always coded by a particular codon. Cells decode mRNAs by reading their nucleotides in groups of three called codons. Thus the number of possible amino acids would be 4 x 4 x 4 64.
There are 61 triplet codes for amino acids. Anti-codons are complimentary to codons.

10 An Rna Codon Table Showing The Mapping From Threeletter Rna Codons Download Scientific Diagram

The Genetic Code Codon Table Article Khan Academy

Synonymous Codons Of 20 Amino Acids Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "How to Decide Which Codon to Use for an Aminoacid"
Post a Comment